How do you know when to recommend a Broda Chair over a Geri Chair?
As occupational therapy practitioners, sometimes making the recommendation for a wheelchair can be hard, especially for a person that doesn’t quite fit the norms of a standard seating and positioning.
So I went right to the source and teamed up with Broda to help answer this question!
But first, let’s define what each of these are.
What is a Broda Wheelchair?
Broda is a wheelchair company that traditionally offers tilt-in-space positioning chairs with the Comfort Tension Seating® system which prevents skin breakdown through reducing heat and moisture for people in any type of healthcare setting, but commonly used in long term care/skilled nursing facilities or home care.
Many times, I choose these products for people that need a high level of positioning or special adaptations due to things such as severe scoliosis, knee contractures, skin breakdown, Huntington’s or if they have had repeated falls.
These products are classified as Durable Medical Equipment (DME) Class1 Mechanical Wheelchairs (IOR), which means in some cases and jurisdictions these chairs and wheelchairs are available for funding! Because they are categorized as DME, they require premarket clearance based on a much more extensive validation, established guidelines and standards, ensuring high safety, mobility and patient outcomes.
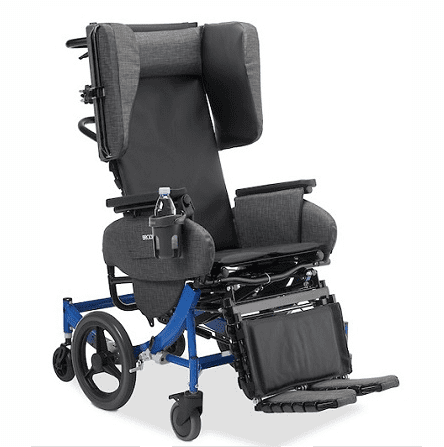


What is a Geri Chair?
Conversely, geri chairs are classified as mechanical chairs (INN) which does not require FDA clearance or testing based on consensus standards. It is designed to allow someone who is mainly in bed, to be able to sit comfortably in a variety of positions while being fully supported.
Many times I may recommend a geri chair because the patient may need a more substantial, and many times less restrictive, seating platform than is provided by a conventional wheelchair.
For clients that are non ambulatory, these can be comfy, roomier, recline and are easier to “lounge” in.
Let’s go through some of the times you would want to use one over the other and then highlight some of the features that I love about them.
When to Recommend Broda Seating:
1. Change in Condition
As the patient’s condition progresses/changes, it is important that they are reassessed to assure they continue to use equipment that will meet their needs, provide them comfort and keep them safe. The need for reassessment can be identified by:
- A decrease in sitting tolerance
- Increased risk for/or development of pressure ulcers
- Decreased ability to self-ambulate and/or self-propel
- Implementing use of restraints to keep patient seated safely, including seatbelts, soft belts, lap trays, etc.
- Increase in postural deviations such as; head drop, lateral lean, slumping and sliding forward while seated
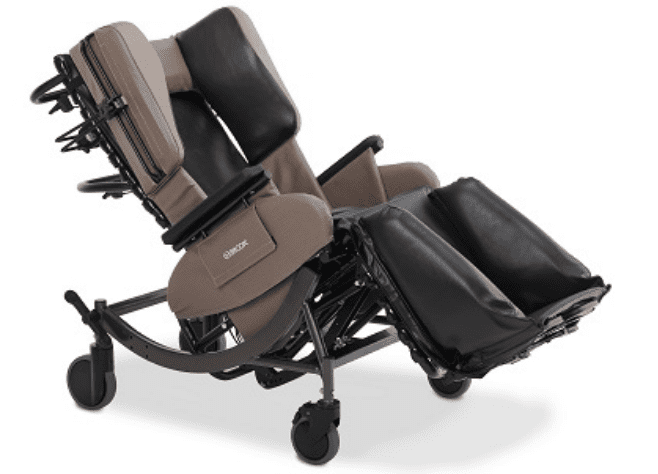

2. Change in Medication (dosage, frequency, etc.)
Patients that are utilizing equipment that no longer meets their needs can result in symptoms and conditions that may cause a change in the use of medications. This can be identified by verbal and non-verbal cues such as:
- Increased reports of pain
- Complaints of new pain
- Behavior changes due to discomfort, pain, and inability to verbalize need
- Increased symptoms such as; swelling of the upper and lower extremities, numbness of the upper and lower extremities, back pain and hip pain
- Increase in use of pain, psychotropic and other medications due to the above

3. “Behavioral” Changes
Prolonged discomfort can cause increased pain and exasperate other symptoms facilitating a change in the patient’s behavior. For patients who are unable to verbalize their needs, these changes may show in the form of frustration or aggression. This can be identified by verbal and non-verbal cues such as:
- New or increased signs of aggression
- New or increased episodes of frustration
- Increased attempts to exit the chair increasing fall risk
- “Behavioral” changes such as aggression, crying, frustration, yelling etc.
- Implementing use of restraints to keep patient seated safely
- Increase in use of psychotropic medications (to calm patient)

4. Increased Time in Bed (Decrease in ADLs and Social Participation)
The patient’s sitting tolerance and ability to socialize may change due to using a wheelchair that no longer meets their needs. Over time, modular seating systems no longer provide the comfort they once did. When patients become uncomfortable sitting in their wheelchair they begin to spend more time in bed potentially increasing their risk for pressure ulcers, fall risks, and other issues.
This can be identified by verbal and non-verbal cues such as:
- Increased pain
- Increase in use of pain and psychotropic medications
- More time spent in bed, inability to socialize (resulting in isolation and depression)
- Postural changes such as slumping, sliding and lateral lean while seated
- Increased symptoms such as; swelling of the upper and lower extremities, numbness of the upper and lower extremities, back pain and hip pain
Why Use a Broda Chair?
1. When comfort is Top Priority
When no other wheelchair can create the comfort required, a geri chair is a good option. It is comfortable for long periods of time and perfect for patients that would otherwise spend most of the day in bed.
2. When a Patient Cannot Tolerate Sitting Upright
If a wheelchair is not comfortable, even in a reclined position, it provides a carepartner to get the person out of bed, be comfortable and enjoy socialization out of the bedroom setting. It’s use is mainly in long term care facilities.

What Size is a Broda Wheelchair?
Depending on the specific type of seating and features you are looking for, the standard sizes are 18″ and 20″ wide with seat depth of 17″. You can also order extra seat depth for larger bodied patients, with sizes increased in 2″ increments such as 22″, 24″, 26″ and 28″ wide. Seat depth can also be increased to 20″, but please note that extra costs do apply for larger sizing.
Some Favorite Features:
- Ability to drop seat height much more than a traditional wheelchair to get the person’s feet in a good position on the floor if they are a “foot ambulator.”
- The Encore Broda Pedal Chair provides a caregiver activated gentle rocking motion for people that need the sensory input to reduce agitation. I have also used this feature to compensate for fluctuating rigidity or spasticity since it “moves” with the patient.
- They are pretty indestructible – I have had some of my most physically challenging patients use these because they have destroyed some of the other wheelchairs due to hypertonicity and severe tremors.
- You don’t need additional cushions! The Comfort Tension Seating feature provides all the pressure relief required.
- It can recline flat! This can certainly come in handy when a carepartners needs to assist in individualized toileting needs.
- Great for people that are difficult to position such as someone with severe kyphosis or chorea due to Huntington’s Disease.
When do you like to recommend using one over the other?